Immunomics Services
Immunomics Services for Macrophages
Macrophages are an important component of the innate immune system and are widely distributed throughout the body in lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissues. CD Genomics offers a wide range of immunomics services targeting macrophages to help clients understand the characteristics, activity, and mechanisms of macrophages and to provide new insights into therapeutic strategies.
M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization
Macrophages are highly plastic and heterogeneous. Depending on the surrounding microenvironment and immune environment, macrophages can acquire different functional characteristics through a polarization process.
M1 Macrophages
M1 macrophages are polarized by Th1 cytokines alone or together with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from bacteria. M1 macrophages are associated with enhanced phagocytic activity, antigen presentation capacity, and increased synthesis and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. M1 macrophages have strong cytotoxic activity against infected cells, scavenging pathogens during infection and mediating resistance to infection.
M2 Macrophages
However, M2 macrophages are polarized by Th2 cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-13. M2 macrophages promote angiogenesis and neointima formation, matrix activation and remodeling, tissue repair, and fibrosis, and often have considerable anti-inflammatory effects. In the context of cancer, M2 macrophages are associated with tumor progression and immunosuppression, thereby negatively impacting patient prognosis.
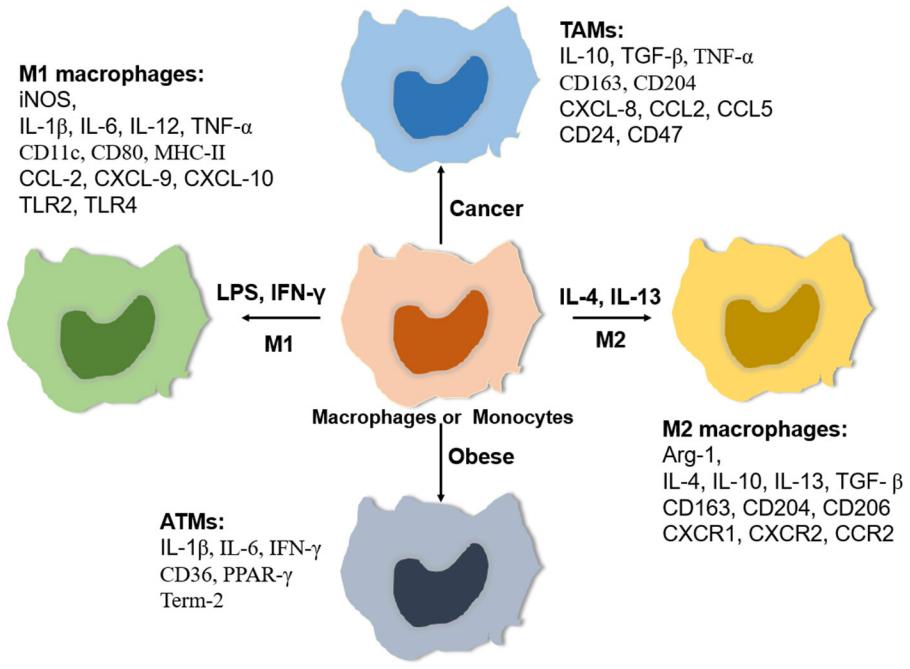 Fig.1 Relative expressing profiles of macrophages or monocytes. (Zhang, C., et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Relative expressing profiles of macrophages or monocytes. (Zhang, C., et al., 2021)
Functions of Macrophages
Macrophages are specialized phagocytes that remove dying or dead cells and cellular debris. In addition, macrophages are capable of regulating innate and adaptive immune responses by secreting cytokines and interacting with other immune cells. Interestingly, macrophages also play an important role in muscle regeneration, wound healing, and limb regeneration. In addition to this, macrophages also play an important role in systemic iron homeostasis, pigment retention and tissue homeostasis.
Immunomics Studies for Macrophages
Studying the polarization and function of macrophages by omics approaches is a favorable research approach. A study has developed a new tri-omics approach using mass spectrometry for large-scale and comprehensive analysis of metabolite, protein, and histone modifications in a single sample. The study reports a complex relationship between arginine, tryptophan, glucose, and citric acid cycle metabolism, protein and histone post-translational modifications, and human macrophage polarization.
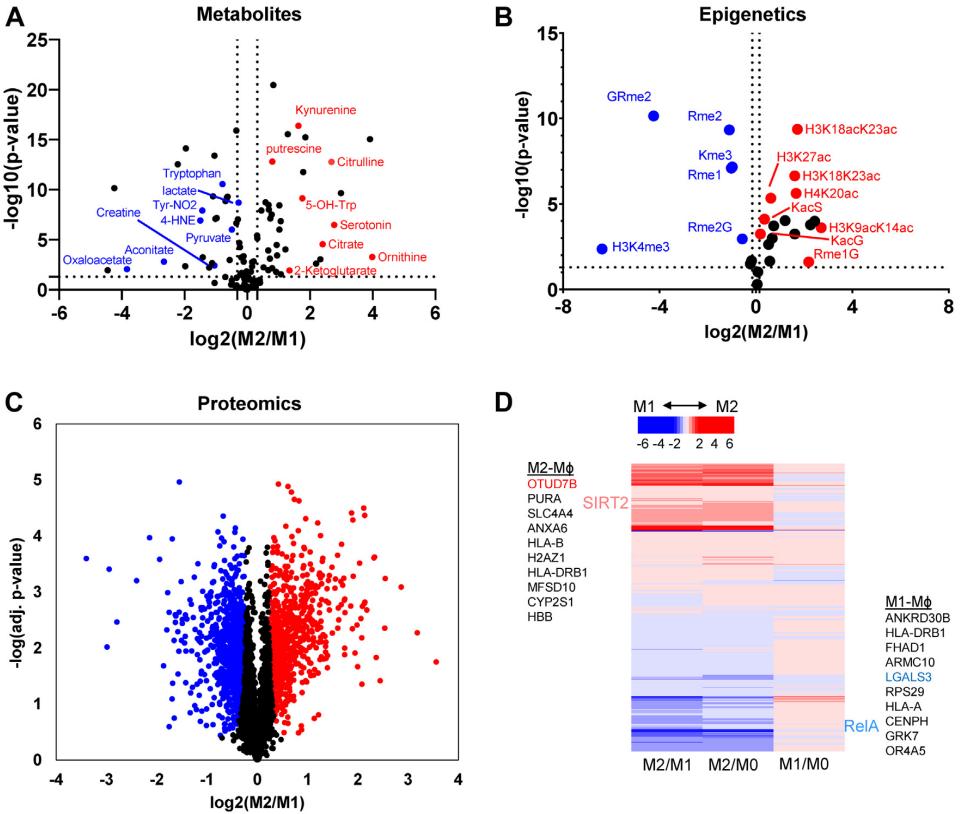 Fig.2 Alteration of metabolites, histone acetylation and methylation, and protein expression in M1 and M2 macrophages. (Sowers, M. L., et al., 2022)
Fig.2 Alteration of metabolites, histone acetylation and methylation, and protein expression in M1 and M2 macrophages. (Sowers, M. L., et al., 2022)
Our Services
Macrophages are important phagocytes that mediate antimicrobial immunity. Macrophages help the immune system to kill pathogens and repair damage such as infections. CD Genomics offers multiple services for analyzing macrophages based on omics to help clients better understand macrophage development, polarization, and function, as well as the development of potential novel therapies.
Why Choose Us
CD Genomics has an advanced omics research platform that focuses on a variety of omics analyses and data processing for the study of immune cells. Our team consists of experts in the field and aims to help our clients design and complete sophisticated solutions. Please contact us for more information.
References
- Zhang, C., Yang, M., & Ericsson, A. C. (2021). Function of macrophages in disease: current understanding on molecular mechanisms. Frontiers in immunology, 12, 620510.
- Sowers, M. L., Tang, H., Singh, V. K., Khan, A., Mishra, A., Restrepo, B. I., Jagannath, C., & Zhang, K. (2022). Multi-OMICs analysis reveals metabolic and epigenetic changes associated with macrophage polarization. The Journal of biological chemistry, 298(10), 102418.
